Daniel Comboni
Comboni Missionaries
Institutional area
Other links
Newsletter
We are now at the second Sunday of Ordinary Time in the liturgical year. After celebrating the Baptism of Jesus last Sunday, today’s Gospel presents the episode of the Wedding at Cana. The feasts of the Magi, the Baptism of Jesus, and the memory of the Wedding at Cana form a triad of “epiphanies” – that is, “manifestations” – which, according to ancient Christian tradition, were part of the feast of Epiphany. (...)
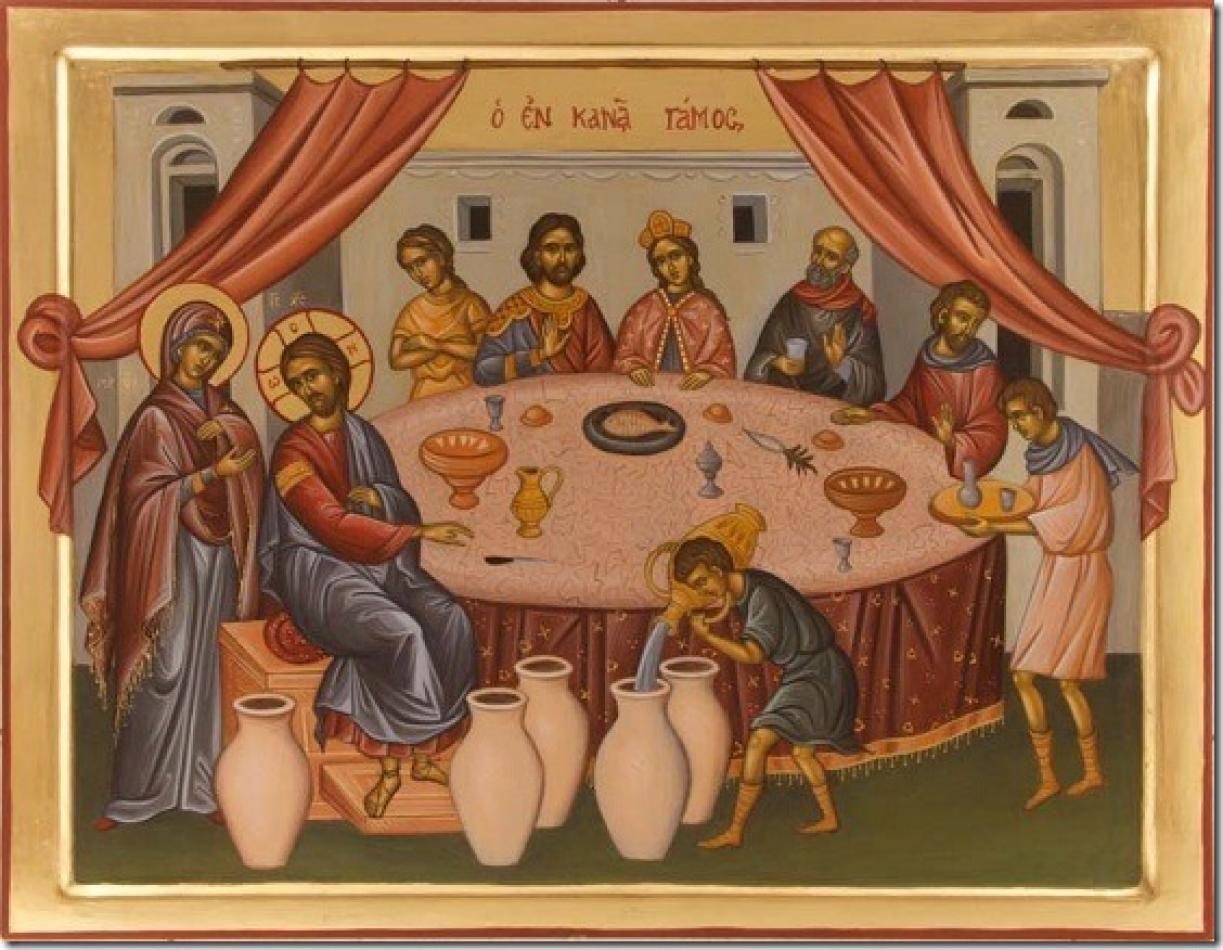
The Wedding at Cana, the third Epiphany
“This was the beginning of the signs performed by Jesus.”
John 2:1-11
We are now at the second Sunday of Ordinary Time in the liturgical year. After celebrating the Baptism of Jesus last Sunday, today’s Gospel presents the episode of the Wedding at Cana. The feasts of the Magi, the Baptism of Jesus, and the memory of the Wedding at Cana form a triad of “epiphanies” – that is, “manifestations” – which, according to ancient Christian tradition, were part of the feast of Epiphany.
The miracle of turning water into wine, which occurred during the wedding of an anonymous couple at Cana in Galilee, a village near Nazareth, is recorded exclusively in the Fourth Gospel. At first glance, it seems to be a simple story. However, the fact that Jesus began his public ministry with such a prodigious act is surprising. What also stands out is the importance the evangelist attributes to this event.
The marginal role of the bride and groom, the focus on Mary and Jesus at the centre of the scene, and the choice of this miracle as “the beginning of the signs” suggest that behind the apparent simplicity of the story lies a deeper meaning. Scholars indeed consider this text a true Johannine masterpiece, rich in symbolism. The story is a refined interweaving of threads that draw on numerous biblical references.
Let us try to draw out some of these threads:
a) The passage begins by stating that it was “the third day” (a detail omitted in the liturgical text). But what exactly does the evangelist mean? In the Jewish context, weddings were celebrated on Tuesday, the third day of the week, which began after the Sabbath. By connecting this “third day” with the previous references to “the next day” (John 1:29, 35, 43), we can discern a symbolic structure: an inaugural week (4+3), echoing the initial week of creation. Furthermore, in the New Testament, the “third day” has a Paschal connotation: it is the day of the Resurrection. The Fourth Gospel was written in the light of the “third day.” We too are called to read our lives in the light of the “third day.” Are we able to see daily events from the perspective of the Lord’s Easter?
b) “There was a wedding at Cana in Galilee, and the mother of Jesus was there.” Why was Mary present? Probably due to a familial connection with the couple. However, the evangelist never mentions Mary’s name, neither in this episode nor at the foot of the cross (John 19:25-27). For St John, the title “mother of Jesus” is an expression of honour that highlights her unique role.
c) “Jesus and his disciples had also been invited to the wedding.” This is the first time in John’s Gospel that the group of disciples is explicitly mentioned. From this moment, they become Jesus’ family and follow him everywhere. We too, as disciples, are invited to this wedding today. Let us note that this first meeting does not take place in the Temple or the synagogue, but in a home, for a celebration, in a secular context. What might the former disciples of John the Baptist, so austere, have thought? And what do today’s “serious” Christians, who see the Christian life solely as sacrifice and renunciation, think? By participating in this celebration, Jesus invites us to rediscover a God who is close, who celebrates life with us. What image of God predominates in my relationship with the Lord?
d) “When the wine ran out, the mother of Jesus said to him, ‘They have no wine.’”Wine is the protagonist of this story. It is a symbol of joy. Why did it run out? Had the bridegroom miscalculated? We must remember that weddings typically lasted about a week. Some blame Jesus, who arrived with a large group of disciples! Mary teaches us here the delicate and precious ministry of intercession: bringing to the Lord the situations where “the wine is lacking,” in the places we frequent.
e) “Jesus said to her, ‘Woman, what concern is that to you and to me?’” This response has sparked much debate. Why does Jesus address Mary as “Woman”? He does so again when entrusting her to the beloved disciple at the cross. It is not a cold or distant term, as it might seem. On the contrary, it is a title laden with symbolic meaning. Think of Eve, the Woman, “mother of the living” (Genesis 3:20). Woman also represents Israel (a feminine word in Hebrew), wedded to God (see today’s first reading). Woman is also the representation of the Church (Revelation 12).
f) “My hour has not yet come.” What hour is this? The beginning of his ministry? In St John’s Gospel, Jesus uses this expression to refer to the hour of his “glorification” on the cross. Here we can perceive a significant divergence between God’s timing and ours. Jesus says to his relatives, who urged him to manifest himself in Jerusalem: “My time has not yet come; your time is always ready” (John 7:6). Is this not sometimes our own expectation, especially in prayer, to try and convince God to adapt his timing to ours?
g) “His mother said to the servants, ‘Do whatever he tells you.’” Mary’s humble trust is moving, as is the edifying obedience of the servants (diakonois), who fill the six jars – symbols of imperfection (7-1) – to the brim. This is true diakonia: doing what the Lord tells us, even when we do not fully understand its meaning!
h) “This, the first of his signs, Jesus performed at Cana in Galilee; he revealed his glory, and his disciples believed in him.” This was the first of seven signs/miracles. The last will be the raising of Lazarus. What is Jesus’ glory? That of the Messiah. Superabundance was the sign of the arrival of messianic times: “The earth will yield its fruits ten thousand times, and a vine will have a thousand branches; each branch will yield a thousand clusters, each cluster a thousand grapes, and each grape will yield a kôr of wine” (Greek Apocalypse of Baruch, apocryphal, 1st century AD). Jesus is the Bridegroom, and at Cana, he already foreshadows the final wedding feast that John will contemplate in Revelation: “I saw the holy city, the new Jerusalem, coming down out of heaven from God, prepared as a bride adorned for her husband” (21:2).
The epiphany of Jesus at the Wedding of Cana invites us to view life as the place of God’s manifestation, learning to read the signs of his presence in the light of the “third day,” the day of Easter.
Fr. Manuel João Pereira Correia, mccj
Loving You is a Feast
Fr. Fernando Armellini
John 2:1-11
At first glance, this passage seems a simple story of a miracle, even if a bit strange, somewhat embarrassing miracle. There are various details that amaze. I try to name a few. John in his Gospel narrates only seven miracles. Is it possible that he had one more interesting to choose? This gesture of Jesus does not seem at all educative. If they had already drunk too much, why provide more wine? The farmers of northern Africa, upon hearing this passage read, commented: “We are at the level of Bacchus.” St. Augustine answered them: the water that comes from heaven revives your vineyards, and this water is transformed into wine; miracles happen every day.
Difficulties are not over: even if it were appropriate to offer wine, why resort to a miracle? It would have been sufficient to take up a collection among the guests.
The first disciples of Jesus had been followers of the Baptist—an ascetic who did not eat and did not drink (Mt 11:18). Faced with an excess of wine, they should not have believed in Jesus, but remain scandalized.
Why does the evangelist John gives so much importance to this episode? He stresses that it was the first of the signs performed by Jesus. The disciples believed and have given their support to the Master in seeing this sign. He employs a solemn expression, that does not occur anywhere else in the New Testament: “Jesus revealed his glory.” For so little? A gesture that perhaps our magicians today would know how to repeat successfully? The evangelist’s annotations seem excessive, inappropriate. They would be more logical, more understandable, for example, after the healing of the man born blind, or after the “resurrection” of Lazarus.
And again, why nothing is said of the main figures of the feast? The bride does not exist at all; the groom has an insignificant role; he does not say a word. The most important of them are the toastmaster, the servants and the jars that are described in every detail (v. 6). One wonders also what so many stone jars were doing in a private home. Were they just for purifications? They can only have but a symbolic meaning because materially they are perfectly useless: the water could be brought directly to the table without going through the jars; it was not worth for the poor servants to draw it twice.
It is not also clear why they speak of the mother of Jesus without mentioning her name, as it happened at the foot of the cross. (Jn 19:25-27). If we had only the Gospel of John we would not even know that she was called Mary.
There is also a mysterious hint on the hour of Jesus. A dramatic hour that gets closer and closer. It will be discussed later in the Gospel of John (John 7:30; 8:20; 12:23.27; 17:1). What is that hour?
Finally, why did Jesus perform the miracle after giving a negative and a little brusque response to the mother?
Too many difficulties to consider this passage as a simple piece of news! Behind the seemingly simple story lies a deeper message.
The Gospel of John is like a vast ocean: it can be contemplated on the surface or in depth. From the shore, the rippling waves, the unfolding of the sails, the reflections of light and color fascinate. But the most intense emotions are for those who have a chance to gear up and go down to the bottom, where the most unexpected and varied forms of life, fish, corals, algae are waiting.
Even with the Gospel of John, one must go to the bottom to capture all the richness of his message. It is what we will try to do today.
In a village in Galilee, a wedding feast is celebrated. There are the guests who gathered to spend a few happy days, but here’s a disappointment: there is no wine and there is not even water because—according to the story—the jars are empty (they will be filled only by order of Jesus). A situation of abandonment, of general sadness. This is the surface. What’s in depth? To descend we must equip ourselves with the tools that are provided by the Old Testament.
The wedding feast
The name Israel is for us masculine, in Hebrew, it is feminine: a chance that the prophets did not miss to introduce in describing the symbolism of marital relationship of their people with the Lord. He—they say—is the faithful husband, while Israel is the bride that often lets herself be seduced by idols, giving her love to strangers.
Here’s how through the prophets God declares his love: “As a bridegroom rejoices in his bride, so will your God rejoice in you” (Is 62:5); “So I am going to allure her, lead her once more into the desert where I can speak to her tenderly … . There she will answer me as in her youth as when she came out of the land of Egypt … . call me: My husband and never again my Baal. I will espouse you in faithfulness” (Hos 2:16-18,22).
These are delightful images that communicate joy, hope, and the will to respond with the same love and the same fidelity to this God who also promises: “Who can abandon his first beloved? The mountains may depart and the hills be moved, but never will my love depart from you” (Is 54:6,10). Yet, in Jesus’ time, Israel had resumed the attitudes of the slave, not of the bride. We will see later what had happened. Now we continue to search for the meaning of the images in the story of the wedding at Cana.
The wine
In the Bible, drunkenness is condemned (Pro 23:30), but wine is a symbol of happiness and love (Ecl 10:19; Ct 4:10). “Wine and music gladden the heart” (Sir 40:20). A feast without wine becomes a funeral: no singing, no dancing, no joy; only long faces, unhappy and nervous people. “What is life without wine?”—asks Sirach (31:27). “Wine gladdens the heart of man”—says the Psalmist (Ps 104:15). “In the streets, they cry for wine: all joy is gone”—says Isaiah (Is 24:11).
At the time of Jesus, Israel expects the Kingdom of God, the kingdom that the prophets have described as a banquet laden with “rich food, and choice wines, meat full of marrow, fine wine strained” (Is 25:6). This kingdom, however, still seems to be far away. The people are sad, like those who celebrate a wedding feast without wine.
Why is she in this condition? The reason is simple: the bride’s rapports with God are no longer there—as the prophets had preached—the bride, who is happy to enjoy the tenderness of her husband. They are those of the slave forced to obey the orders of the master. The religion taught by the rabbis is that of “merits.” Who acquires them and is faithful to the law is loved by God. To help people to observe it, the spiritual leaders begin to give the interpretation: they specify, point out, define, stand up to reduce the Word of God to a code of standards, an inextricable maze of provisions of detailed little rules impossible to observe.
Since transgressions are inevitable, and one always feels unclean and guilty, the purification rites were devised. The ritual baths for which having always convenient water at the disposition is essential. Water is not at all easy to get because it cannot be transported with containers, but must flow through special canals.
Here is the symbolic significance of the six empty stone jars: they represent the religion of purification, that set of practices and rituals unable to communicate serenity, joy, and peace. Not from this water, but from what Jesus orders to draw—his water—that will result in the best wine.
The wedding at Cana without wine represents the sad condition of the people of Israel disappointed and dissatisfied, which replaced the momentum of love for the Lord with the fulfillment of legal provisions. This way of relating with God never gave joy, yet it is an always present temptation. People rely willingly on religious practice, the strict observance of duties, the repetition of rituals of which they do not even know the meaning.
Jesus’ mother can be Mary, yes, but she can also indicate the spiritual community in which Jesus was born, and from which he was educated. In today’s passage, she certainly represents the pious people of Israel, those who first realize that the religious situation they live in is unsustainable. What must they do then? They do not have recourse to the head of the table, that is, the religious leaders who proved to be unable to organize a real feast, but to Jesus. They understand that the living water comes only from him. Whoever drinks it, is transformed into wine, that is, rendered happily.
John places this “sign” at the beginning of his Gospel because it is a synthesis of all that Jesus will do later. He is the one who will celebrate the wedding feast with the community.
His hour has not yet come because he is only at the beginning of his public life. The feast has begun but will culminate when “his hour will come,” (Mt 24:36) when, on Calvary, he will manifest all his love by giving his life for the bride when from his pierced side will flow “blood and water” (Jn 19:34). In Cana, he makes only a sign of what we will do. In the hour when he will “pass from this world to the Father” (Jn 13:1) he will actually give the water “welling up to eternal life” (Jn 4:14).
Fernando Armellini is an Italian missionary and biblical scholar.
https://sundaycommentaries.wordpress.com